Home > Legal perspective
Approximately 17% of the world’s population is visually challenged, 2.6% has an intellectual disability, and 1% require a wheelchair for mobility. Considering the growing importance of web accessibility vis-à-vis the increasing population with varying degrees of disabilities, the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) created Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) to provide an actionable framework.
Standard Accessibility Guidelines
World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) created Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) to provide a universal actionable framework
- WCAG 2.0 is a gold standard version
- WCAG 2.1 is the extension of WCAG 2.0
- W3C releases the first draft of WCAG 3
Accessibility Laws
WCAG 2.0 was the gold standard and served as a foundation for international accessibility laws. In several countries across the world, governments are mandating change and starting to enforce compliance with accessibility regulations like ADA, WCAG 2.1, and Section 508.Noncompliance is no longer an option
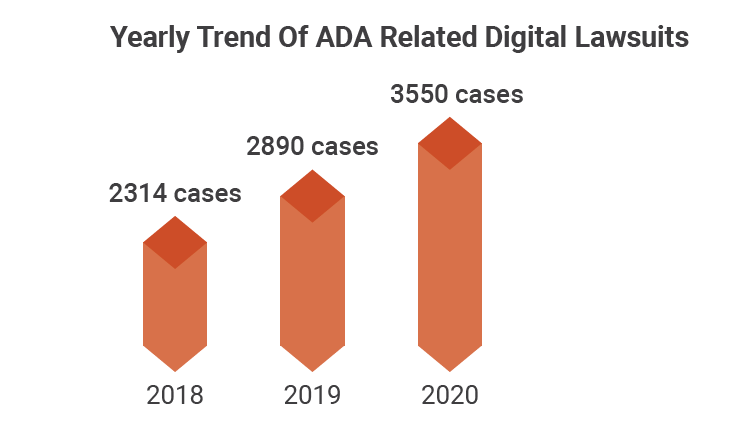
Accessibility needs to be addressed in the near term as you run the risk of facing lawsuits and negative brand impact. Lawsuits are steadily on the rise. ADA related cases in 2020 increased 23% over 2019.
Accessibility Global Laws
USA
- Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
- Section 508 – Rehabilitation Act of 1973
Canada
- Accessible Canada Act (ACA)
- Accessibility for Ontarians with Disabilities Act (AODA)
UK & Europe
- European Accessibility Act (EAA)
- Web Accessibility
- Directive
- EN 301 549
- Equality Act 2010
- Disability Act 2005
Australia
- Disability Discrimination Act (DDA)
